Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms
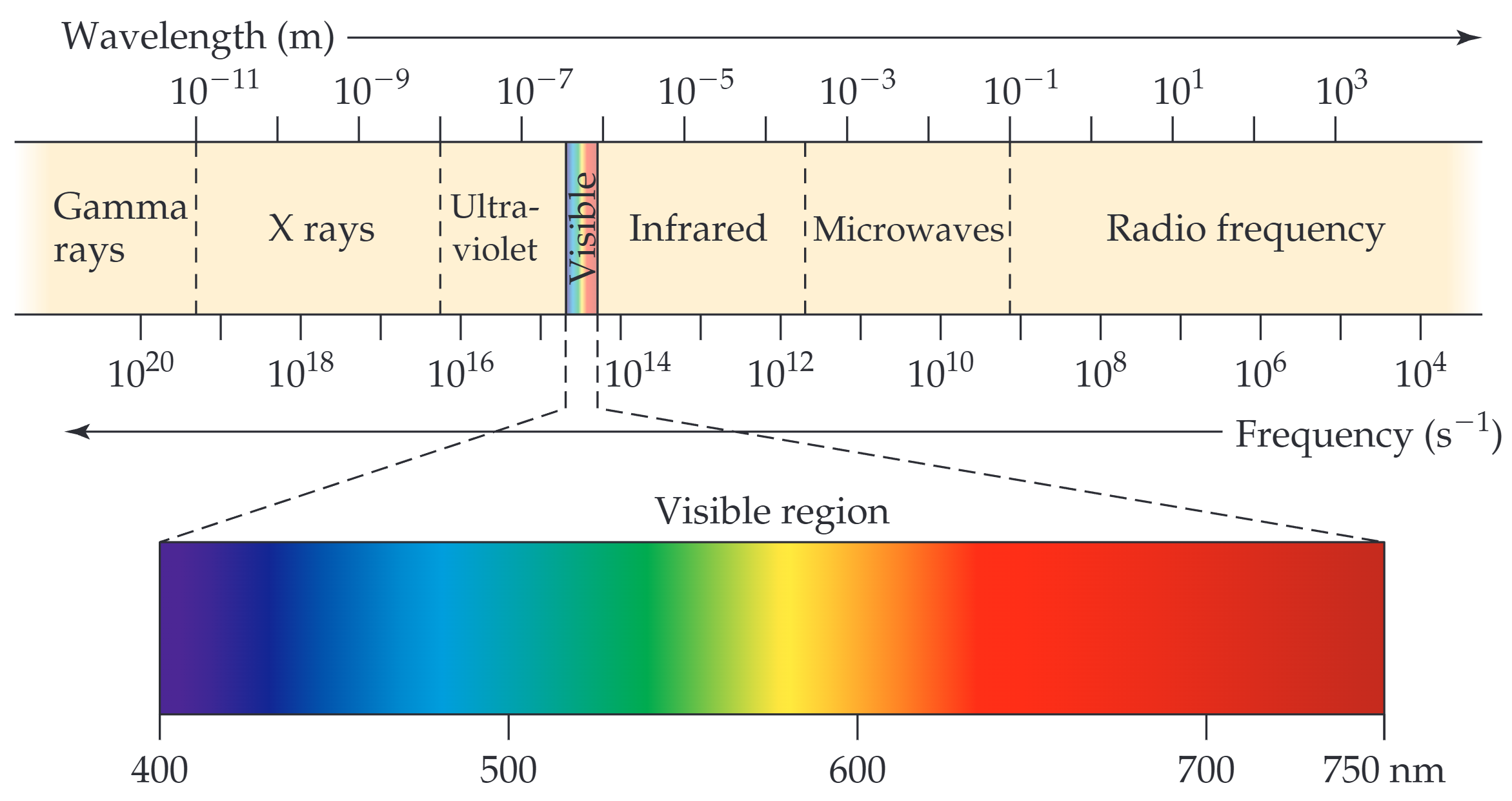
光的波动性
\[ \lambda \nu = c \]
连续光谱
黑体辐射——普朗克
\[ E = h \nu \]
光电效应——爱因斯坦
\[ \text{Energy of photon} = E = h \nu \]
Rydberg equation
\[ \frac{1}{\lambda} = (R_H)\left(\frac{1}{n_1^2} - \frac{1}{n_2^2}\right) \]
线光谱——玻尔
玻尔模型的三个假设
- Only orbits of certain radii, corresponding to certain specific energies, are permitted for the electron in a gydrogen atom.
- An electron in a permitted orbit is an “allowed” energy state. An electron in an allowed energy state does not radiate energy and, therefore, does note spiral into the nucleus.
- Energy is emitted or absorbed by the electron only as the electron changes from one allowed energy state to another. This energy is emiited or absorbed as a photon that has energy \(E = h \nu\).
玻尔模型的氢原子能级公式
\[ E = (- h c R_H)\left(\frac{1}{n^2}\right) \]
物质的波动性——德布罗意
\[ \lambda = \frac{h}{mv} \]
测不准原理——海森堡
\[ \Delta x \Delta (mv) \geq \frac{h}{4 \pi} \]
波动方程——薛定谔
超纲内容
\[ \psi(x, y, z) \]
Probability Density or Electron Density
\[ \psi^2 \]
Pauli Exclusion Principle
No two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers \(n, l, m_l, m_s\).
Hund’s Rule
For degenerate orbitals, the lowest energy is attained when the number of electrons having the same spin is maximized.
量子力学原子模型
\[ n, l, m_l, m_s \]